
Published:
Readtime: 7 min
Every product is carefully selected by our editors and experts. If you buy from a link, we may earn a commission. Learn more. For more information on how we test products, click here.
We’ve long heard about the health benefits of Vitamin D, but what exactly does that encompass? Put simply, vitamin D is your body’s response to sunlight. Contrary to most other vitamins that are found exclusively within foodstuffs, the ‘Sunshine Vitamin’ is a product of your skin meeting the suns rays head-on and turning them into an essential component for life. It dissolves into your body fat and has a number of essential functions.
Of particularly interest, once Vitamin D is absorbed into the body your body cannot instantly process it. Instead, like a hormone, this vitamin acts as a catalyst in two different reactions, called ‘hydroxylations’ before being processed and consumed. The reactions themselves are where the body finds the most benefits.

Benefits of Vitamin D
It’s a secret ingredient in essential chemistry the body acts out upon itself. Because of this tiered process to the bodies absorption of Vitamin D, it’s found in 3 forms in the body. These are called D-1, D-2 and D-3. For the most part these are incredibly similar, particularly D-2 and D-3.n They only differ in the shape of their makeup which allows them to bond to different parts within the gut, which is where the vast majority of Vitamin D breakdown actually occurs. Here are the commonly accepted health benefits of Vitamin D:

1. May Fight disease
Within the body you need Vitamin D for a number of reasons, perhaps the biggest use is in the regulation of the immune system. It directly interacts and bolsters the utility of the cells that fight infection within the body. A low amount of Vitamin D within the body has a direct correlation with an increase in cold and flu’s.
There have also been studies finding that can aid in the prevention of bronchitis and pneumonia, but it’s a hotly debated topic with no clear outcome as to whether a high count truly does aid lung health. Despite the lack of clarity over whether Vitamin D in high amounts can help your immune system, it’s ubiquitously understood that a low count will harm your ability to bounce back from sicknesses.

2. May Reduce Depression
Vitamin D has a link with depression for two reasons, the first is found anecdotally and in observation. This is the fact that during winter months, when the sun hides away for great stretches of the day, depression tends to spike. Taking supplements can work towards fighting these depressive episodes, but there are a huge number of factors that come into play.
In general SAD (seasonal affective depression) comes in a wide number of forms, the lack of sunlight definitely playing into the reasons that we, as humans, find ourselves sadder in the winter months, but there’s also a pretty common-sense link between it being cold and dark, and humans not feeling their best. In cases of persistent depression there have been studies showing that increasing Vitamin D intake can improve mood, but it’s far from a one-stop shop to ‘fixing’ your emotions.
The second large link that Vitamin D has with depression is its ability to combat tiredness and fatigue. This is a bit of a chicken and egg situation, in that deficiency can cause you to feel lethargic and lacking in energy. Treating that at its root cause can bolster your ability to go out into the world, or even get up out of bed. This is a more effective way of treating a symptom of depression in an attempt to overcome it. The link between Vitamin D and fatigue is a definite one there are multiple examples of chronic daytime fatigue and headaches being treated with supplements.

3. May Boost Weight Loss
Vitamin D is definitely something you should consider if you’re on a weight-loss mission. It has numerous effects on the body that can make the difference when cutting the kilos is on the table. Firstly, it has an appetite suppression impact on the body. When taking Vitamin D supplements the body finds itself increasing calcium in greater amounts, this process has been shown to reduce feelings of hunger. To double down on this effect, taking calcium in conjunction with the vitamin was found to lead to a greater weight loss in a study done against a placebo.

Symptoms of a Vitamin D Deficiency
From the above, you can summarise what a few of the impacts of not getting enough Vitamin D might be. Where science is a little baffled, and what causes so much of the ‘potential’ effects, is that deficiency of it can lead to an insanely wide range of outcomes on the body.
While taking Vitamin D in excess may, or may not, be a panacea, lacking it will definitely cause some oddball effects. These include:
- Tiredness, pain and a general sense of malaise with the inability to work out what exactly is wrong.
Muscular pain and weakness, extending to pain in the bones which can cause problems climbing stairs, getting up off the floor or even cause you to waddle. - Stress Fractures, particularly in the legs.
- Bone problems, it is essential in the maintenance and growth of bones.
Vitamin D deficiency is searched for as part of a standard medical examination and blood test. If your blood count is found to be low you’ll probably be X-rayed to make sure your bones are strong enough. Additionally you’ll be recommended to take supplements and ensure you’re getting enough sun.

Vitamin D Supplements
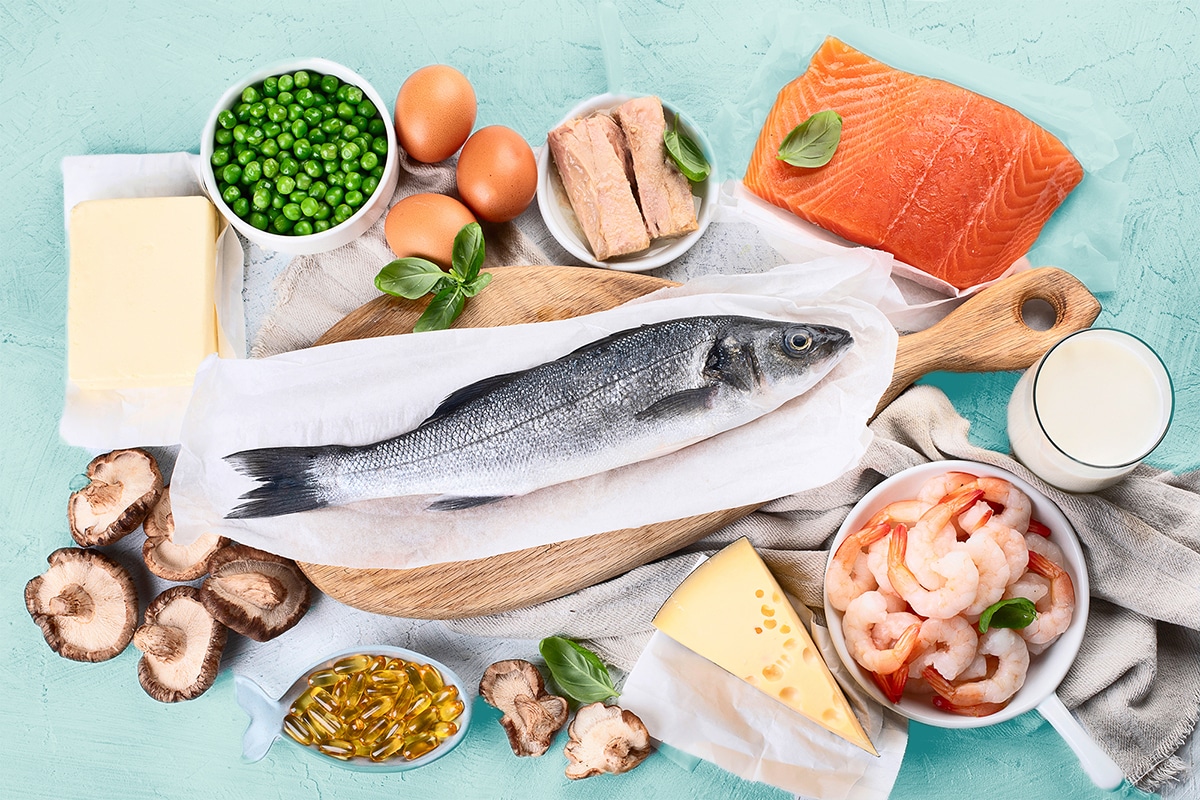
There are foods that contain Vitamin D, but they are few and far between. Your best bets are oily fish (Salmon, Sardines, Herring), egg yolks, liver and shrimp.
Understanding the lack of naturally occurring Vitamin D, a number of foods will be fortified and have it added. If you ever see fortified versions of milk, cereal, yogurt and orange juice you can be certain that they’ve got added Vitamin D and will be a healthy addition to almost any diet. Finally, fish oil and Vitamin tablets are guaranteed ways to increase your intake.

How Much Do You Need?
This is where much of the back and forth over Vitamin D intake comes from. It’s an ever-changing school of thought, where the findings consistently seem to suggest we need more than previously thought.
However, to add to the constant maelstrom that is nutritional study, The Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences utilises a different measurement system to work out how much you should be taking. They use an ‘international unit’ IU. As it currently stands, it’s believed that 10-20 micrograms per decilitre is the healthy amount. This equates to 400-800 IU.
But there is a strong push within the nutritional world that counters this idea, and instead recommends you should be looking at 25-100 mg, which is 1000-4000 IU. With all the conflicting data, the main takeaway, if you’re worried you may be Vitamin D deficient, is to head to your local doctor for a blood test and a check-up. But eating more fish will never hurt!
General FAQs
Vitamin D is an essential micronutrient with multiple uses. It’s synthesised in the skin as a reaction to sunlight but can be found throughout the body.
Benefits of Vitamin D are incredibly wide ranging. It’s two biggest benefits are in ensuring you have strong, healthy bones. It’s an essential component in a healthy immune system. It can be a mood elevator and stave off tiredness and fatigue. There are also links to it’s abilities as a weight modulator.
There are many! Supplements exist in the form of fish liver oil tablets, as an oral supplement to take in pill form and a wide range of foods are ‘fortified’ with additional Vitamin D.






























Comments
We love hearing from you. or to leave a comment.